
Healthy marine ecosystems and climate stability have always been closely interlinked. One affects the other, and we are seeing this play out on a planetary scale. Climate change is partly the result of the extended mismanagement of oceans, but the inverse is true as well. If we have concrete measures in place to preserve, restore and sustainably manage ocean ecosystems, nature becomes a powerful ally that breathes life into climate mitigation, adaptation and resilience efforts.
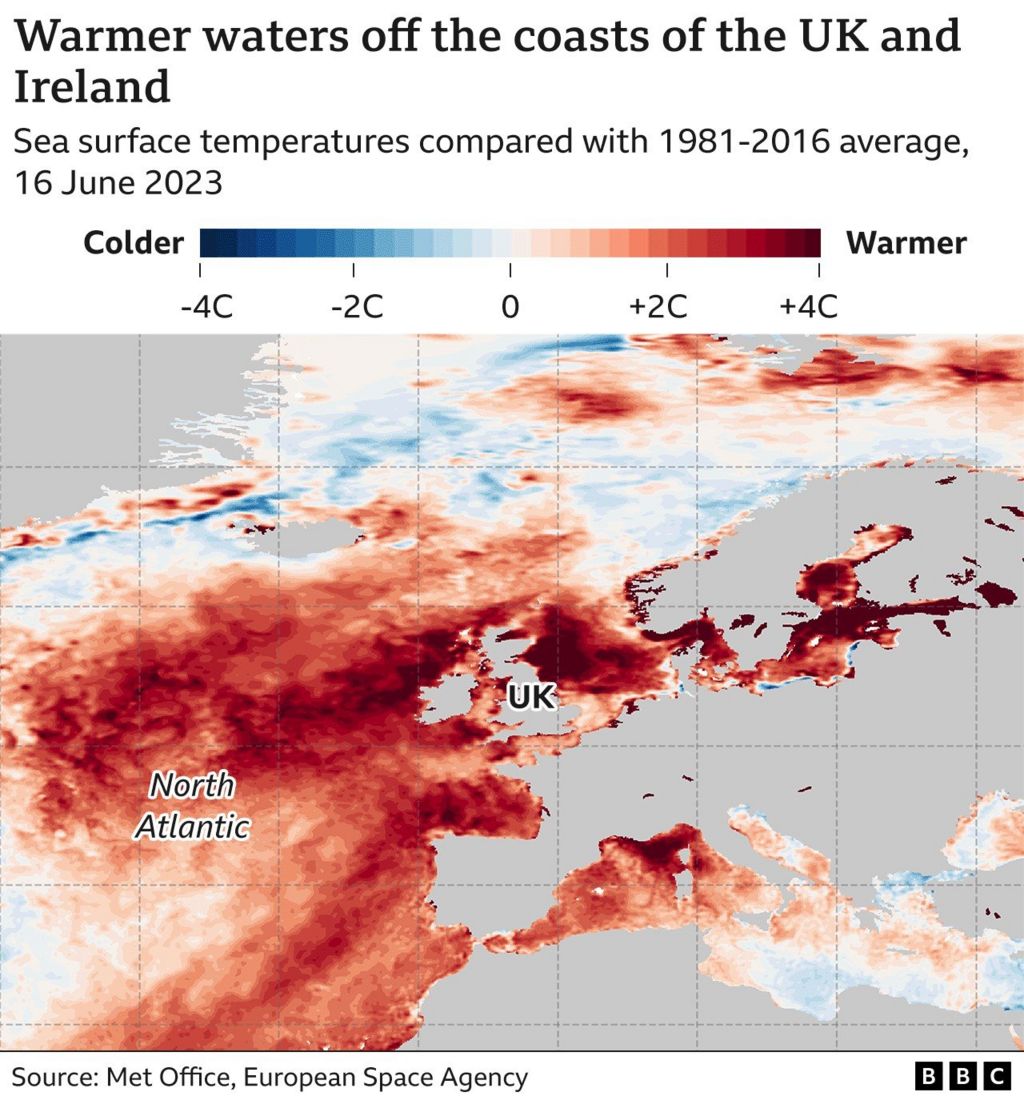
Average ocean surface temperatures broke several records in July, with no signs of slowing down...
Read More












Social Profiles